1. Insufficient endogenous synthesis, requiring external supplementation
1) Low activity of key enzymes in synthesis
Taurine is mainly synthesized in the body through enzymatic reactions of sulfur-containing amino acids such as methionine and cysteine. But the enzyme has low activity in the human body, with its own synthesis only meeting 30% to 40% of normal needs, and the rest needs to be obtained through food or supplements.
2) Strong dependence on transport proteins
Taurine relies on the transport protein TauT to enter cells. If TauT function is impaired (such as gene mutations or aging leading to decreased expression), even with sufficient exogenous intake, cells may still be in a deficient state and require additional supplementation to maintain balance.
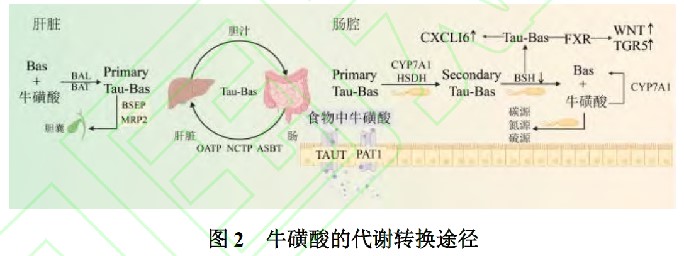
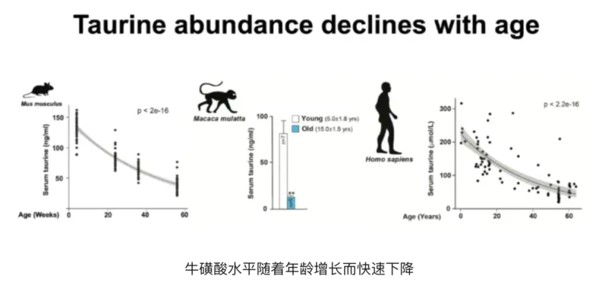
2. Aging leads to a significant decrease in levels, which is associated with age-related diseases
As individuals age, the taurine content in their bodies decreases.
The taurine level of 60 year old people is only 1/3 of that of 5 year old children, and this decline is significantly related to obesity, diabetes, hypertension and decreased immunity.
3. The demand for special physiological stages has surged
1) Fetal and Infant Development
Taurine is a key substance for the development of the brain and retina, accounting for 50% of the total amino acids in the retina. Lack can lead to degeneration of photoreceptors and abnormal differentiation of nerve cells, affecting cognitive and visual functions. Due to the immature synthesis ability of infants, they need to rely on external supplementation of breast milk or formula milk.
2) High metabolic or disease state
Exercise consumption: After exercise, taurine levels can increase to 1.16 times, and supplementation can alleviate fatigue and enhance antioxidant capacity.
Disease recovery: such as myocardial ischemia and liver injury, taurine repairs tissues by regulating calcium homeostasis and antioxidant activity. Lack of taurine in gastric cancer patients can promote tumor immune escape, and supplementation can enhance T cell anti-cancer ability.